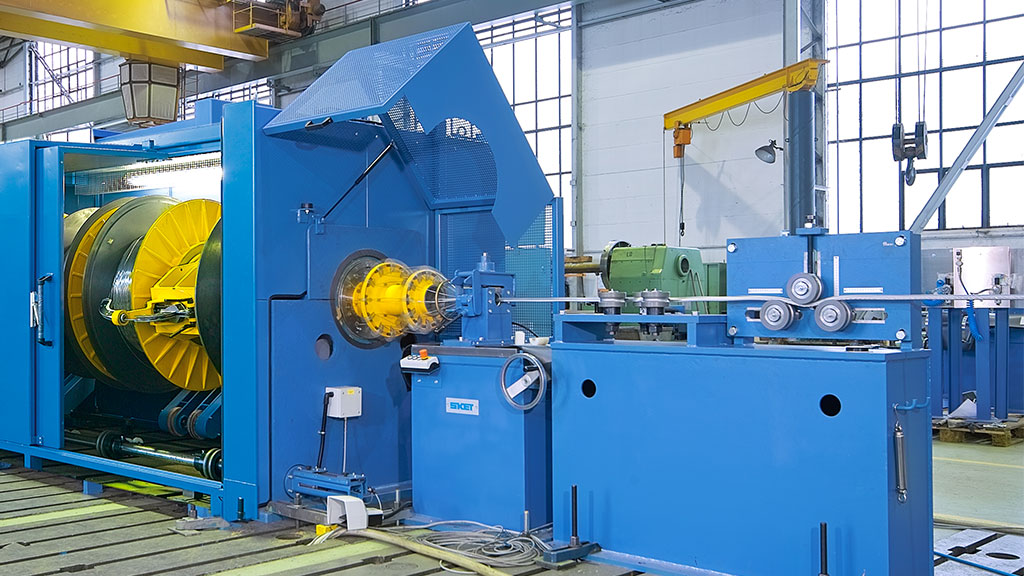
SKET Verseilmaschinenbau GmbH in Magdeburg can look back to a 100 year long tradition in the manufacture and supply of equipment for the wire and cable industry and wide ranging experience in this very specialised area of machine building. Already in the nineteen-eighties SKET systematically revolutionised the production of copper and aluminium stranded conductors in the cable industry with the introduction and development of the Central Strander.
Since then, cable manufacturers throughout the world have been able to gain practical experience of the benefits related to this machine system. 100 such stranding systems around the world are proof of this.
And now the new range of MKZT/S Central Stranders sets new and previously unthinkable standards in the production of overhead lines of all designs and standards. Stranding cage speeds of up to 500 rpm and a pay-off bobbin capacity of around 510 kg, some three times more than was previously possible, bring about productivity benefits which were previously unimaginable. Dependent on the technological needs of the application, the stranding units are fitted with either mechanically or pneumatically controlled flyer systems, so ensuring a product of the highest quality.

The SKET Central Strander is mainly used for:
- the manufacture of round or sector shaped compacted copper or aluminium wire conductors
- the production of overhead cables (ACSR, AAC, AAAC)
- the screening of electric cables
- the armouring of electric cables
Machine Layouts – Progressive Stranding Technology
Unlike conventionally designed rigid stranding machines, the bobbins in the Central Strander are concentric to their axis of rotation. Resultantly, there is no longer a need to load and unload full bobbins of wire. The machines are available in two design versions.
Twin-Version MKZT
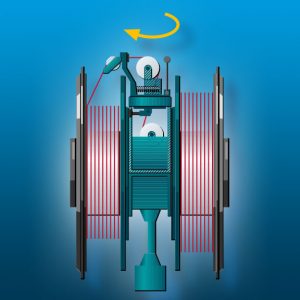 For each wire, two bobbins are arranged one each to the right and the left of the flyer. The flyer is arranged to pivot and can be positioned to pay the wire off either the right-hand side or left-hand side bobbin. The bobbin not currently in use as the pay-off bobbin can be wound with wire. Stranding and bobbin winding occur simultaneously. Downtimes are kept to a minimum and the machine output is maximised.
For each wire, two bobbins are arranged one each to the right and the left of the flyer. The flyer is arranged to pivot and can be positioned to pay the wire off either the right-hand side or left-hand side bobbin. The bobbin not currently in use as the pay-off bobbin can be wound with wire. Stranding and bobbin winding occur simultaneously. Downtimes are kept to a minimum and the machine output is maximised.
Single-Version MKZS
 Each wire is associated with one bobbin only and with one flyer. Stranding and bobbin winding operations alternate. The winding speed is several times that of the stranding speed resulting in long production cycles. The Single Version is considerably shorter than the Twin Version. It is particularly useful for machines stranding large numbers of wires.
Each wire is associated with one bobbin only and with one flyer. Stranding and bobbin winding operations alternate. The winding speed is several times that of the stranding speed resulting in long production cycles. The Single Version is considerably shorter than the Twin Version. It is particularly useful for machines stranding large numbers of wires.
State of the Art Drive Technology
The machines are mainly driven by frequency controlled three-phase motors, providing separate drives to the stranding carriage, haul-off and take-up. Digital control technology enables the infinitely variable lay-length to be set from the control desk. Speeds can be varied infinitely, within prescribed technological limits, during the operation of the machine.
State of the Art Ancillary Equipment
- stationary or traversing pay-offs and take-ups for bobbins having a flange diameter of up to 4,000 mm
- haul-off technology based mainly on double-capstan haul-offs, tailored to the requirements of the customer and having a pull of up to 200 kN.
- Single capstan and belt type haul-offs also available.
- pre- and post-formers to suit the technological characteristics of the stranding material or finished product
- taping heads to provide water proofing or semi-conductive layers
- compacting heads for the production of sector shaped conductors
State of the Art Automation Technology
- touch screen control via programmable controllers provides fully automatic process control and operation, machine monitoring, programme
- management, data recording and storage, service functions and maintenance
- speed and angle synchronisation, torque and traction contro
- maintenance of all product related quality parameters at all times ensured by controlled machine braking, including in the event of an electrical
- failure (AC drive versions)





